The HPC4 is the fourth-generation high-performance computing cluster implemented and maintained by ITSO. It is officially rolled out in mid-Oct 2024 after a pilot testing period. Hosted in the new High Performance Infrastructural Center (HPCIC), the HPC4 equipment is primarily funded by the University, while also accepting contributions from faculty members. The HPC4 platform is designed to support scientific computations with Intel-based and AMD-based CPU nodes, and it also features Nvidia-based GPU machines for tasks that do not require hardware specific for AI centric workloads like HKUST SuperPOD.
HPC4 usage is charged based on a charging model. For details, please visit Charging/Pricing Model of HPC4
7x24
HPC4 Highlights
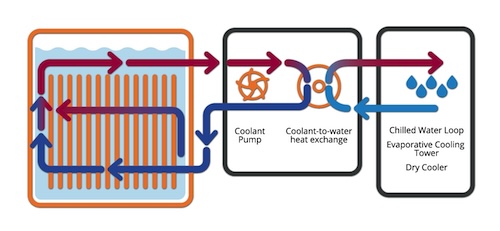
The HPCIC adopts Liquid Immersion Cooling Technology, which offers the following advantages:
• Allows higher density of computing resources resulting in more hardware in less physical space.
• Offers high energy efficiency for sustainability
• Operating cost reduction from energy saving in cooling of machines

The system environment of HPC4 is based on Rocky Linux 9. Secure computing approach would be adopted, with regular operating system upgrades and security patches to be applied to maintain a safe environment for research workloads.
User Documentation
New to our HPC environment? We provide a comprehensive HPC Handbook.
This documentation serves as a central knowledge base for AI and HPC users, offering detailed guides on:
- Getting Started: Account setup and connecting to the cluster.
- Job Scheduling: How to submit and manage jobs using SLURM.
- Software Environment: Guides for Python, R, MATLAB, Java, and module management.
- Operating System: Navigating the Linux environment.
HPC4 Hardware Specification
The HPC4 cluster consists of multiple types of node, each with distinct hardware configurations to cater to a variety of computational needs. The specifications for each type of nodes are detailed below.
CPU Nodes
| Processor | Nodes | CPU Cores / Threads (per Node) | System Memory (per Node) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Intel Xeon Platinum 8592+ | 10 | 128 Cores / 128 Threads | 512GB DDR5-5600 ECC |
| AMD EPYC 9754 | 76 + 1* | 256 Cores / 256 Threads | 768GB DDR5-4800 ECC |
| AMD EPYC 9754 | 18* + 12^ | 256 Cores / 256 Threads | 1.5TB DDR5-4800 ECC |
GPU Nodes
| GPU Model | Host CPU (per Node) | Nodes | GPUs (per Node) | GPU Memory (per GPU) | System Memory (per Node) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NVIDIA A30 | 2× Intel Xeon Gold 6448Y | 15 | 4 | 24GB HBM2 ECC | 512GB DDR5-4800 ECC |
| NVIDIA L20 | 2× Intel Xeon Gold 6548Y+ | 5 | 4 | 48GB GDDR6 ECC | 512GB DDR5-4800 ECC |
| NVIDIA RTX 4090D | 2× Intel Xeon Gold 6448Y | 10* + 2 | 6 | 24GB GDDR6X | 512GB DDR5-4800 ECC |
| NVIDIA RTX 5880 Ada | 2× Intel Xeon Gold 6448Y | 8 | 6 | 48GB GDDR6 ECC | 512GB DDR5-4800 ECC |
* Contributed servers. Not yet available to public use.
^ To be available soon.
Shared Resources
Performance Comparison
To give an idea of the performance of CPUs and GPUs in HPC4 with others, please check here.
HPC4 Account Application
All HKUST faculty members are eligible to apply for a HPC4 account. To apply, please complete the HPC4 Account Application Form. Students who wish to utilize HPC4 should consult their supervisors to support their applications by completing the above application form.
Getting Started
How to login to the cluster
Click here to view the instructions on how to get access to the HKUST HPC4 cluster
Use of SLURM Job Scheduling System
The Simple Linux Utility for Resource Management (SLURM) is the resource management and job scheduling system of the cluster. All jobs in the cluster must be run with the SLURM.
Click here to learn how to submit your first SLURM job
Click here to view details of using SLURM
Partition and Resource Quota
Click here to view more information on partition and resource quota.
Storage Types
Click here to view more information on different storage types.
HPC4 Software Environment
The software environment promotes a Do-It-Yourself installation approach using Spack and Apptainer, providing the flexibility to customize their software environment.
Modules
Lmod is used to manage installations for most application software. With the modules system, the shell environment can be set up to give access to applications and make running and compiling software easier.
Click here for details of the module system.
Spack - User-managed software installation manager
Spack is a package manager that helps building and managing multiple versions and configurations of software.
Click here for details of Spack.
Use of Apptainer (Singularity)
Apptainer (formerly known as Singularity) container lets user run applications in a Linux environment of their choice. Apptainer literally enables BYOE (Bring-Your-Own-Environment) computing in the multi-tenant and shared HPC cluster.
Click here to view details of Apptainer (Singularity)
HPC4 Policies: Charging & Contribution
Charging Model
Charging for HPC4 services ensures efficient resource allocation and sustainability. It encourages accountability and fair usage among researchers.
Click here for details on the charging for use of HPC4.
Contribution Model
Subject to HPCIC resource availability, the HPC4 adopts community cluster model similar to HPC3 and accepts hardware contribution from faculty members on regular basis.
Details of the HPC4 contribution model are available here.
